Hi, my name is Brady Lilley. I live in Mesa, Arizona but was born and raised in Prescott, Arizona. Yes, I pronounce Prescott like Preskitt like any TRUE Arizonian would...just saying...I am a country girl through and though. I love small towns, dirt roads, and actually being able to go star seeing at night. I am the youngest out of 3 kids, and have one niece who is the apple of my eye. My family is my everything, and no you don't have to be blood to be family.
I am excited to start my career as a teacher! I am currently attending Mesa Community College and Northern Arizona University Extended Campus to make my dreams of becoming a teacher a reality!!! I can't wait to teach! I currently work for Gilbert Public Schools at Desert Ridge Junior High School. I'm a paraprofessional specialist in a multi-disability classroom, and I also work with several autistic students as well. I love my job and wouldn't change it for the world!!!
Wednesday, March 4, 2015
Tuesday, March 3, 2015
Activities
Here are some great websites with fun, interactive games on graphing!
http://pbskids.org/cyberchase/math-games/bugs-in-the-system/
http://www.kidsmathgamesonline.com/numbers/mathdata.html
http://www.abcteach.com/directory/subjects-math-graphing-647-2-1
http://www.the-best-childrens-books.org/teaching-graphs.html
•Searching on Pinterest, I also found some really great ideas!!!
http://pbskids.org/cyberchase/math-games/bugs-in-the-system/
http://www.kidsmathgamesonline.com/numbers/mathdata.html
http://www.abcteach.com/directory/subjects-math-graphing-647-2-1
http://www.the-best-childrens-books.org/teaching-graphs.html
•Searching on Pinterest, I also found some really great ideas!!!
http://www.the-best-childrens-books.org/teaching-graphs.html
http://www.themeasuredmom.com/7-ways-to-make-a-graph-with-kids/#_a5y_p=1925658
http://www.childcarelounge.com/blog/dr-suess-birthday-ideas/
http://www.simplycenters.com/2012/04/jelly-bean-math-activities-freebie.html
All of these sites got my wheels turning!! I can't wait to teach these ideas!!!!
Monday, March 2, 2015
Box and Whisker
| -A box-and-whisker graph is a graph that shows how far apart and how evenly data are distributed it looks like this Minimum: is the lowest extreme of your data. Lower quartile: is the median of your data starting at the minimum to the median of the original data. Median: is the middle of the first set of data Upper quartile: is the median of data starting AFTER the median of first set of data to the maximum.  |
This video I found was very helpful in explaining how to make a box and whisker plot.
http://youtu.be/CoVf1jLxgj4
Sunday, March 1, 2015
Videos and Pages
I think videos are a great resource!! Here are some videos I found very helpful!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h3QoquxnfZk
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qj2CF1XQDMY
Loved these sites!
http://www.mathgoodies.com/glossary/term.asp?term=box-and-whisker%20graph
http://www.mathsisfun.com/data/graphs-index.html
http://mrnussbaum.com/coolgraphing/
-Loved this site because it gives graphing print outs and its all set to common core standards!!!
Friday, February 27, 2015
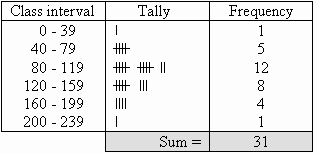
Finding mean, median, mode, and range...

VOCAB!
-As you can see from the image above, I have the vocabulary words. I like this picture because it's a great print out for the classroom, and is super cute!!! I am however going to go and list my definitions as well.
Mean: also known as the average. To get the average you add all the data together then divide the sum by the number of data given.
Median: is the middle. If you don't have a middle number you add the two numbers in the middle of your data and divide by 2. You do however, need to make sure that your data is in least to greatest order.
Mode: this is the data that occurs most frequently.
Range: is the difference between the smaller and biggest number of the data.
How did she get the mean?
-You add up all the data then divide by the number of data given.
-Total data given: 9
*13+13+13+13+14+14+16+18+21=135
-Now take 135 and divide it by 9
*135/9=15
What about mode?
-You can have more than one mode. If 14 was repeated 4 times, like 13 is, then you would have two modes.
How did she get the range?
-The range is the Biggest number subtracted by the smallest number.
21-13=8
Wednesday, February 18, 2015
All About That Graph
-An important part of displaying data are visual
illustrations. These visual
illustrations are different types of graphs.
Graphs such as: pictographs, circle graphs, pie charts, dot plots (also
known as line plots), scatter plots, stem and leaf plots, frequency tables,
histograms, bar graphs, and line graphs.
-First lets take a look at some vocabulary you will
see.
-Categorical
Data: data that represents characteristics of object or individuals in groups.
-Numerical
Data: Data collected on numerical variables.
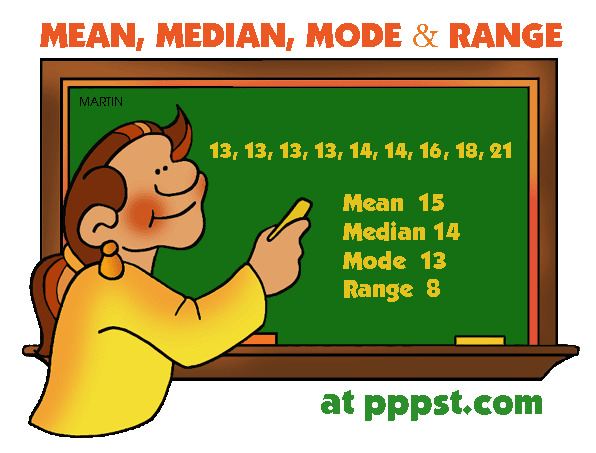
-Pictographs:
used to represent tallies of categories.
 |
-Dot
Plots/Line plot: provide a quick simple way to organize data. Only use them when there is only one group of
data and have less than 50 values.
-Outlier:
a point whose value is significantly greater than or less than others.
-Cluster:
Isolation group of point
-Gap:
large space between data points
-Mode: Data value3s hat
occur the most often
-Stem
and Leaf Plot: a
display where the data is organized by place value.
-Grouped Frequency Table:
Shows hoe many times data occurs in a range.
-Histogram: Compare number of
data items grouped in numerical intervals.
Order does matter.

-Bar Graph: Compare number of
data in grouped categories. Order doesn’t matter.
-Circle Graphs: Circular region partitioned into sections. Each section equals a part or
percentage of the whole.

-Line Graphs: Consecutive data
points are connected by line segments.

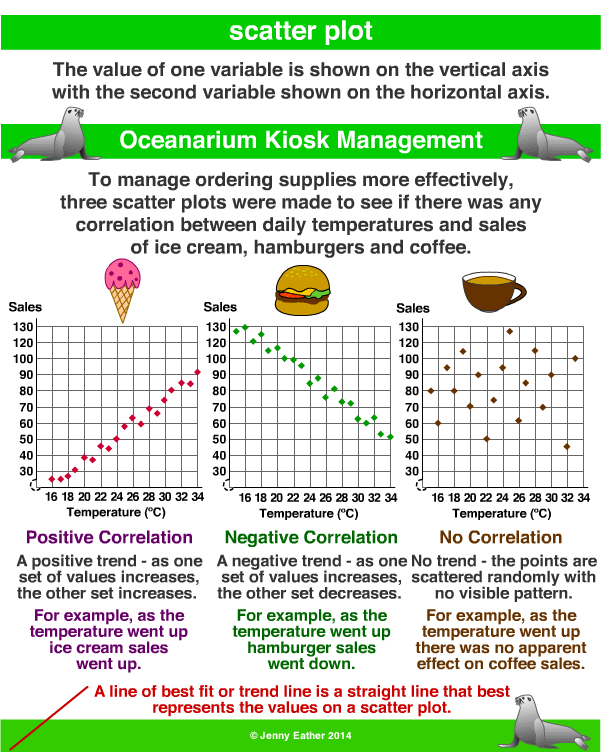
-Scatter Plots: Relationship between
variables cannot be depicted by a broken line.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)